Author: 〇Nasoori Alireza1,2
Affiliation: 1北大 院獣医、2北大 院歯
Abstract:
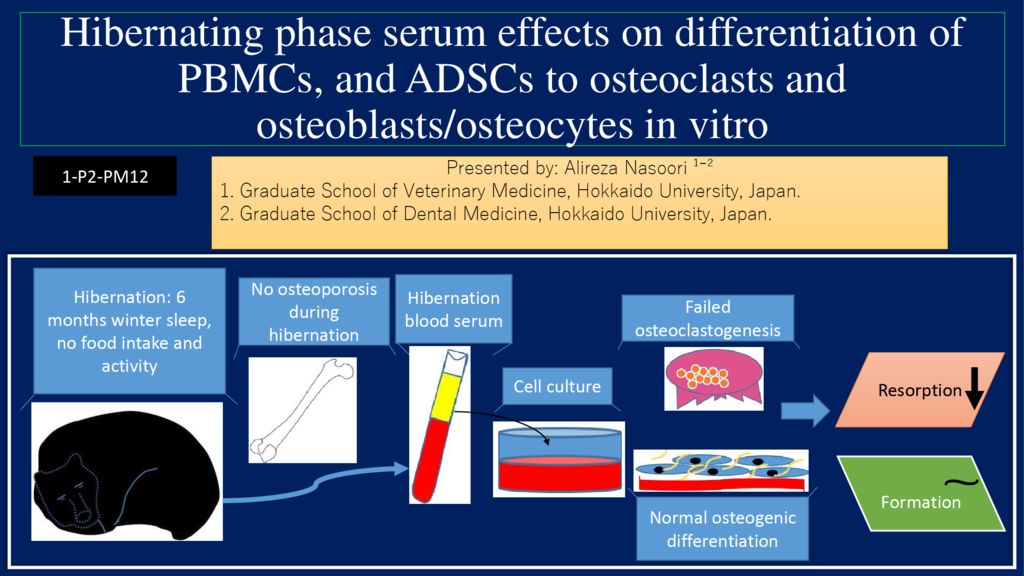
Bears do not suffer from osteoporosis during hibernation which is associated with long-term inactivity, lack of food intake, and cold exposure. The effects of hibernating bear serum on cells to preserve bone mass have not been investigated yet.
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and adipose derived stromal cells (ADSCs) collected from 3 bears were separately cultured with 10 percent serum of active (4 bears for PBMCs and 7 bears for ADSCs culture) and 10 percent serum of hibernating bears (4 bears for PBMCs and 7 bears for ADSCs culture). Osteoclastogenic differentiation was induced by treatment of PBMCs with MCSF and RANKL for 11 days. For osteogenic differentiation of ADSCs, the cells were cultured in osteogenic medium for 34 days. PBMCs and ADSCs were incubated at 37 degree Celsius with 5 percent CO2. The effect of serum type was assessed by microscopic images and staining techniques.
PBMCs that were cultured with the active bear serum containing medium (ABSM) differentiated to multi-nucleated osteoclasts, and were positive for TRAP stain. However, cells supplemented with hibernating bear serum containing medium (HBSM) failed to form OCs, and showed significantly lower TRAP stain (p less than 0.001). On the other hand, osteogenic differentiation of ADSCs was similar between ABSM and HBSM (p more than 0.05) in 3 intervals within 34 days.
It was revealed that osteoclastogenesis of PBMCs is hindered by HBSM, but osteogenic differentiation is ongoing similarly with both ABSM and HBSM implying underlying mechanisms for bone maintenance during hibernation in bears. In addition, this study for the first time showed the formation of bears osteoclasts in vitro and elucidated the effects of bears serum on cell culture in vitro.
 メールで問い合わせ
メールで問い合わせ

コメント